This is an old revision of the document!
Table of Contents
RC Servo
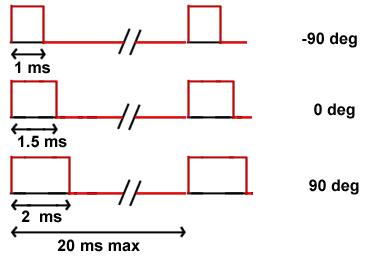
Servo motors are often used in radio-controlled (RC) models, and are very useful in many kinds of small robotics applications because they are compact and inexpensive. An RC servo motor includes a built-in DC motor, gearbox, position feedback sensor (usually potentiometer), and drive electronics. RC servo motors can be controlled by an external pulse-width modulation (PWM) signal. If a signal meets RC servo timing requirements, it usually “describes” a (target) position input for the servo drive electronics. Servo motor electronics compare the shaft position with the inputted position, trying to find a shaft position where they match. The position control signal is a continuous square-wave signal, as depicted in figure.
Servo motors have three wires:
- Red = Power supply Vcc (4.8–6V)
- Black = Ground
- White/yellow = PWM input (may vary type-by-type)
The PWM signal has the following shape:
1.0ms = farthest left position
1.5 ms = center position
2.0 ms = farthest right position
Electrical connection
Table of motor drive signals from ATmega128 to the actuator board.
Electrical connections
- Make sure all power is off.
- Connect the actuator board and main board with a 26-pin cable.
- Connect the RC servo motor to the actuator board, as shown in Figure 2.
Note: The signal wire (usually yellow or white) is towards the outer edge of the board.
- Connect the JTAG converter with the ATmega128 main board and the PC.
- Finally connect the power to the main and actuator boards.
Example code
/*------------------------------------------------------------- Title: RC Servo motor with Actuator Board Date: 080327 Ver.: 1.1 Compiler: AVR-GCC Target: ATmega128 Hardware: ATmega128 controller board, Actuator board, RC servo motor Author: Raivo Sell 2008 Notes: Description: Moves slowly RC motor shaft from one edge to another. ---------------------------------------------------------------*/ #define F_CPU 14745600UL //CPU Frequency (influences delay function) #include <avr/io.h> #include <util/delay.h> ///////////////// Main function ////////////////////////////////// int main (void){ // Set timer control registers TCCR1A = _BV(COM1A1) | _BV(COM1B1) | _BV(WGM11); TCCR1B = _BV(CS11) | _BV(WGM13) | _BV(WGM12); DDRB = 0x30; // PB5 & PB6 output ICR1 = 36000; // Sets the upper limit to Timer1 //(creates 50 Hz signal) XTAL/8/256*50 14745600 OCR1A = 2700; // Sets when the PWM signal should toggle. while(1){ for(OCR1A=500;OCR1A!=5000;OCR1A++) {_delay_ms(3);} for(OCR1A=5000;OCR1A!=500;OCR1A--) {_delay_ms(3);} } }